Audiology is a distinct field of medicine about the identification, assessment, and management of disorders in hearing, balance, and other parts of the neural system. An audiology professional is called an “audiologist.”
An audiologist helps newborns and older adults with their hearing problems. Commonly, they are the ones who are consulted by people who are hard of hearing due to aging, injury, exposure to excessive noise, viral infections, and other factors that affect hearing.
What does an audiologist do?
Health care professionals who specialize in audiology use technologies and their socializing abilities to identify and treat hearing, balance, and other auditory problems in patients. They help patients with problems in communicating and connecting with the world. Here is a list of what audiologists do:
- The ability to identify, examine, diagnose, and treat disorders with hearing, balance, and others
- Interpretation and explanation of test results that are understandable by patients
- Give health advice to patients about the current state of their hearing and address the need for further treatment and management
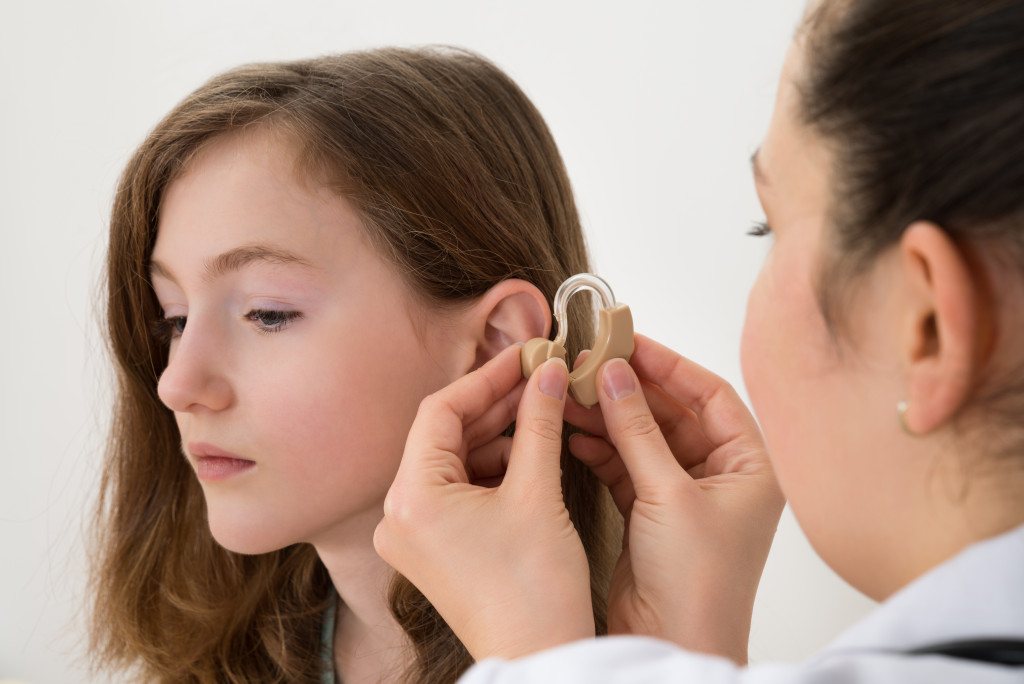
- The knowledge to help a patient acquire the best hearing aids and cochlear implants by providing correct fitting, programming, and hearing rehabilitation
- Observe and conduct hearing screening programs for people of all ages with perceived hearing problems
- Study a patient’s ability to take in spoken language to identify if there are problems with their hearing
If you are looking for a specialist to help you with your auditory problems, audiologists are the best ones to consult.
What does it take to be an audiologist?
Audiologists go through a four-year program that immerses them in various classroom, research, and learning environments. They are put in clinical settings to experience and learn from actual patient cases. The clinical settings involve newborns, children, older adults, and older adults. The varied population in which to-be audiologists are exposed provides them with adequate knowledge and experience in dealing with auditor problems that can be attributed to age and special medical conditions.
Individuals studying audiology have the following in their knowledge base:
- Anatomy of hearing
- Epidemiology
- Statistics and research methods used in audiology
- Acoustics
- Nervous system and ear disorders
- Pediatric audiology
- Hearing loss prevention
- Hearing aid assignment
- Hearing counseling
- Speech-reading
Their vast and encompassing knowledge and skills base make gives them the versatility they need to help patients and direct them to the correct specialists if their problems are outside of their scope as medical professionals.

How are they different from ENT specialists?
Ear, nose, and throat or ENT specialists are medical school graduates with otolaryngology specializations. They are often found diagnosing and treating ear, nose, throat, and lower skull area disorders. ENTs commonly work with audiologists in the same offices because their expertise can be combined to address problems that make two specializations in medicine converge.
Is a career in audiology a good one?
According to Business Insider, audiology was rated among the top 16 careers with good financial compensation and work-life balance. Among the 16 professions on the list, audiology came in sixth. The list was filled mostly by professions from the health care sector.
Audiology, similar to other careers in medicine, compensates very well but comes with licensure and board certification requirements for specialists to practice legally. Audiologists also undergo various exams to practice, coupled with a doctor of audiology (AuD) degree.
1,615 licensed and practicing audiologists in the United States were surveyed, and it was found that the median compensation for these medical professionals is in the 83,000-dollar range. However, the number does not encompass audiologists practicing in primary and secondary school settings.
A career in audiology is an excellent choice for medical school prospects—it is stable, and the demand remains high even with the invention of impressive technologies that help with hearing problems.
Where do audiologists practice?
Audiologists typically practice in clinical settings and ENTs and practice under audiology clinic networks like HH Acquisitions that help them manage practice effectively. These networks take the work off of clinics’ backs regarding staff management, general customer service, and procurement of equipment for diagnosis and treatment.
How prevalent is hearing loss?
In the U.S. alone, 13 percent of individuals aged 12 and older has hearing loss in both ears, based on hearing examinations conducted. In adults, 2 percent aged 45 to 54 years are with severe hearing loss, making them unable to participate in daily activities. For people aged 55 to 64 years, 8.5 percent have hearing loss.
Hearing loss may come from issues at birth, exposure to extreme levels of noise, injuries, and some illnesses.
A career in audiology sounds like a stable one, but it does not come without challenges. A successful career in this field of medicine requires years of study, practice, and continuous learning, as with all medical fields.